International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are a number of international accounting standards for a number of transactions and events in financial statements, governing how certain types of financial transactions and events are reported.
The aim of the standards is to have a single accounting language to understand business from company to company and from country to country.
These standards also allow companies and investors to make informed financial decisions, so that companies can easily understand these standards before making investment decisions.
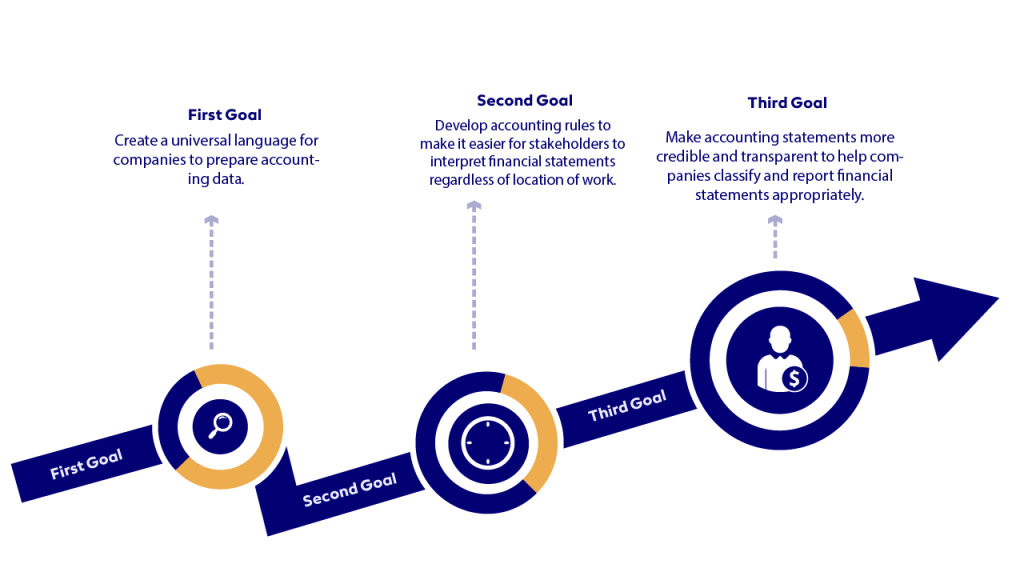
These standards have been developed to achieve a number of objectives:
- Create a universal language for companies to prepare accounting data.
- Develop accounting rules to make it easier for stakeholders to interpret financial statements regardless of location of work.
- Make accounting statements more credible and transparent to help companies classify and report financial statements appropriately.
Benefits of International Financial Reporting Standards
Companies located in IFRS countries benefit because investors are more willing to make investment decisions after verifying information about the company transparently and clearly according to fixed and specific standards. It is easy to make comparisons and study financial statements.
International Accounting Standards (IAS) work on:
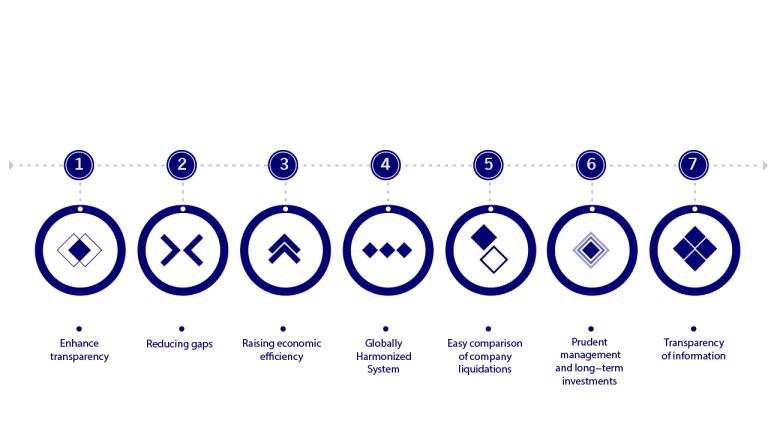
International Accounting Standards (IAS) provide a high set of internationally recognized accounting standards to achieve transparency and efficiency in financial markets globally. It enhances international comparability and quality of financial information and enables investors and partners to make economic decisions.
These standards help reduce the information gap between business officials and partners in money, as these standards make it easier for money owners to have the information needed to hold management accountable.
IFRS contributes the information needed to help investors identify opportunities, avoid risks around the world, and avoid waste of capital.
Also, for companies, the use of a single, reliable language reduces the cost of capital and international reporting costs.
The goal of establishing common standards and rules is to standardize and rationalize the presentation of accounting information that can meet the hypothetical needs of many users.
As a result, it contributes to improving accounting practices and enhancing space-time comparisons in terms of financial information.
Due to the standardization of global accounting standards, it is very easy to compare the economic results of two companies by reviewing financial statements that follow consistent standards despite the country’s differences.
IFRS is a viable reference system, and therefore it is possible to provide a common reference system for interpreting and comparing financial information.
One of the advantages of applying IAS is the ease of coordination between different sectors and providing the greatest possible transparency in financial communications.
IAS should meet three main values:
- Completeness: It must include the financial activities of the entire company.
- Comparability: where the financial statements are consolidated and identical for all companies.
- Impartiality: Non-alignment and to have the last word on the figures in the reports.
Disadvantages of International Accounting Standards
Although there are many advantages in international accounting standards, they are not without some disadvantages and problems, including:
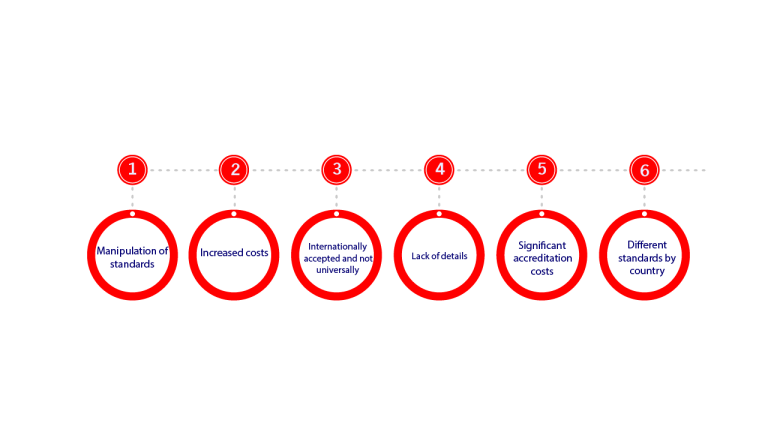
The flexibility offered by international standards to prepare has negative aspects, as it allows companies to use only the methods they want, i.e. they can show only the financial statements they want. This can enable revenue or profit manipulation or concealment of financial problems or fraud.
Small businesses have to adopt the same standards as large companies, and therefore small companies have to have the same human resources as large companies and this means costs greater than the volume of work.
International Accounting Standards are not applied in the USA, as they follow their own standards, and this makes it difficult to prepare the financial statements of multinational companies if one of them is in the USA.
Everyone relies on the financial reporting system, which requires disclosure of the company’s financial position annually, and this information must be provided with certain criteria that allow auditors to examine it. Each country adopts its own number of standards in financial reporting.
However, when IFRS was developed, the specifics of each country had to be waived from the others, so that it was possible to have fixed standards that fit all countries.
All companies in countries that adopt the new standards must start providing adequate training to the staff to be able to work with the new standards, and this means an additional cost for companies operating at the national level only because this means that the cost of training on the new standards is greater than the benefits accruing to it.
For example, in some countries businesses may rely on bank financing to raise capital, meaning that their financial statements emphasize prudence and a strong balance sheet.
In other countries the business relies on the sale of shares and this means a different type of financial information required.
List of IFRS standards
- 1: Adoption of IFRS for the first time
- IFRS 2 Stock-Based Payments
- IFRS 3 Business Integration
- IFRS 4 Insurance Contracts
- IFRS 5 Non-Current Assets Held for Sale and Cessation of Operations
- IFRS 6 Exploration and Evaluation of Mineral Resources
- IFRS 7 Financial Instruments: Disclosures
- IFRS 8 Operating Sectors
- IFRS 9 Financial Instruments
- IFRS 10 Consolidated Financial Statements
- IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements
- IFRS 12 Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities
- IFRS 13 – Fair Value Measurement
- IFRS 14 Deferred Regulatory Accounts
- IFRS 15 Revenue from contracts with clients
- IFRS 16 Leases
- IFRS 17 Insurance Contracts
- IAS 1 Presentation of financial statements
- IAS 2 Inventory
- IAS 7 Statement of cash flows
- IAS 8 Accounting Policies, Changes in Accounting Estimates and Errors
- IAS 10 Events After Report Period
- IAS 11 Construction Contracts
- IAS 12 Income Taxes
- IAS 16 Property, Plant and Equipment
- IAS 17 Leases
- IAS 18 Revenue
- IAS 19 Employee Benefits
- IAS 20 Accounting for
- Government Grants and Disclosure of Government Assistance
- IAS 21 Effects of changes in foreign exchange rates
- IAS 23 Borrowing Costs
- IAS 24 Related Party Disclosures
- IAS 26 Accounting and reporting by retirement benefit plans
- IAS 27 Separate Financial Statements
- IAS 28 Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures
- IAS 29 Financial Reporting in Economies with High Inflation
- IAS 32 – Financial Instruments: Presentation
- IAS 33 EPS
- IAS 34 Interim Financial Reporting
- IAS 36 Impairment of assets
- IAS 37: Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets
- IAS 38 Intangible Assets
- IAS 39 – Financial instruments: recognition and measurement
- IAS 40 Real Estate Investment
- IAS 41 Agriculture
- Inline CTA
AHG is a leading regional auditing and chartered accounting firm, present in the GCC and North Africa. Since 2014, AHG has helped companies operating in the UAE to maximize success. We are fully prepared to help your business in the UAE through a team of trained tax experts to prepare your business for corporate tax in the UAE.
AHG-Dubai Group serves a wide range of clients and multinational companies. This comes in light of the company’s strategy to focus on two main pillars: geographical expansion in frontier markets and driving a positive community culture. By combining our strengths and expertise in the region, we offer our clients best-in-class services tailored to their needs to maximize their investment goals in a rapidly changing environment.

